Condition
Aortic Coarctation
What You Need to Know
Aortic coarctation is a congenital heart defect. It means the aorta is narrower than it should be.
Key Symptoms
The symptoms of aortic coarctation can vary from mild to more severe. The most common symptoms are:
- Trouble breathing
- Poor weight gain
- Pale skin
- Sweating
- Cold feet or legs
- High blood pressure
Diagnosis
Doctors typically diagnose aortic coarctation by:
- Physical examination
- Chest X-ray
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Echocardiogram
- Cardiac catheterization
- CT scan
- MRI
Treatment
Treatments may include:
- Cardiac catheterization
- Surgery
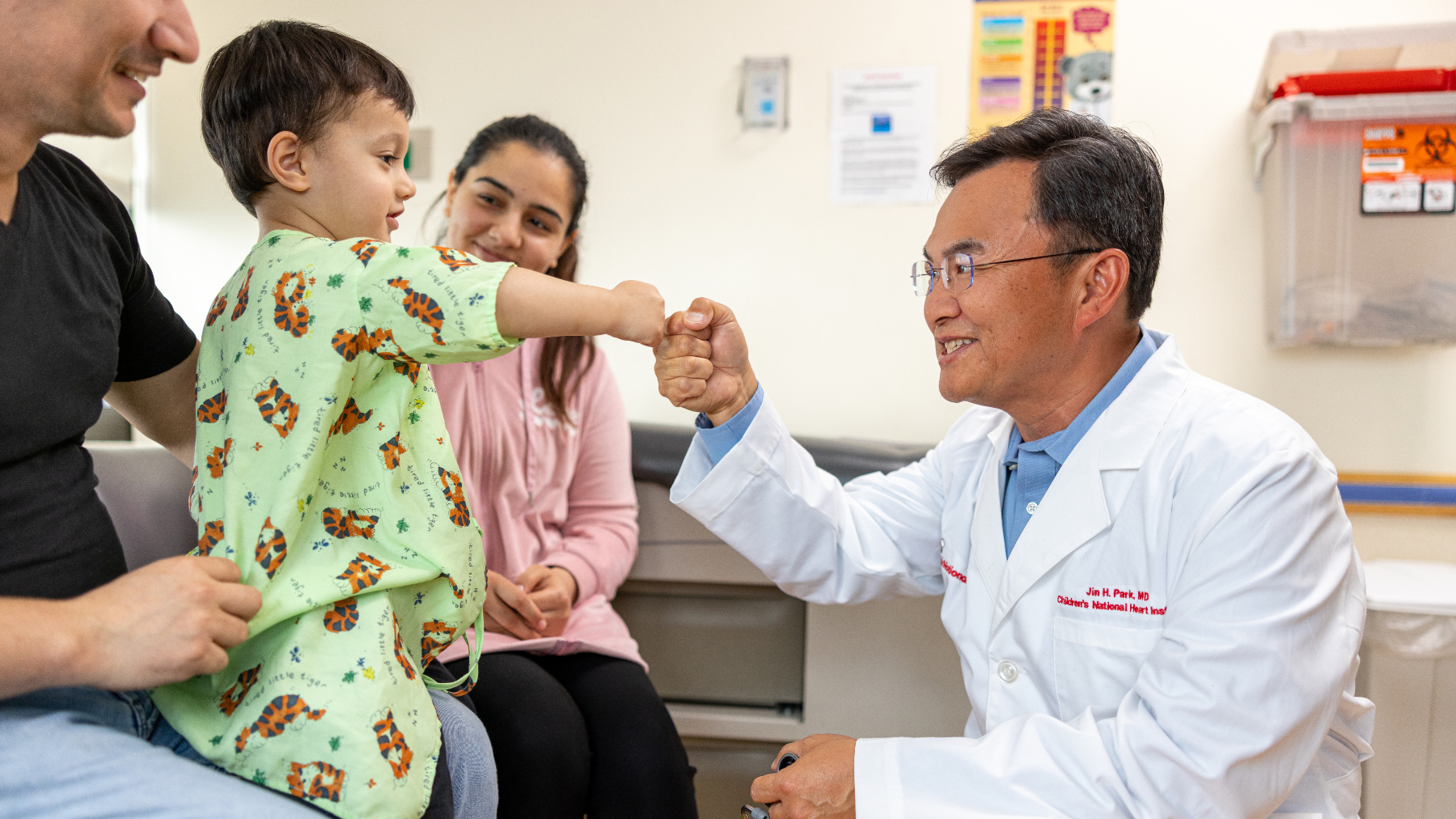
Schedule an Appointment
Our pediatric specialists provide personalized care for your child’s physical, mental and emotional health needs. Meet our providers and schedule an appointment today.
Frequently Asked Questions
Prevention and Risk Assessment
What is coarctation of the aorta in children?
What causes COA in a child?
What are the symptoms of COA in a child?
Diagnosis
How is COA diagnosed in a child?
Treatments
How is COA treated in a child?
What are possible complications of COA in a child?
How can I help my child live with COA?
When should I call my child's healthcare provider?
Aortic Arch Coarctation Surgical Outcomes
Learn about some of the lifesaving surgeries our pediatric heart experts perform each year at Children's National. Find outcomes data here.
Meet the Providers Who Treat Aortic Coarctation
Departments that Treat Aortic Coarctation

The Zickler Family Prenatal Pediatrics Institute
The Zickler Family Prenatal Pediatrics Institute at Children's National Hospital in Washington, D.C., provides specialized care for babies during pregnancy, delivery and after birth.

Help Kids and Make a Difference
Invest in future cures to help children have brighter futures.