Condition
Pediatric Sickle Cell Disease
What You Need to Know
Sickle cell disease is an inherited blood disorder characterized by defective hemoglobin (a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to the tissues of the body).
Key Symptoms
The most common symptoms of sickle cell disease are:
- Anemia
- Yellowing of the skin, eyes and mouth (jaundice)
- Pain crisis, or sickle crisis
Diagnosis
Doctors typically diagnose sickle cell disease by:
- Blood tests
Treatment
Treatment may include:
- Pain medicine
- Blood transfusions
- Stem cell transplant
Meet the Providers Who Treat Sickle Cell Disease
Frequently Asked Questions
What is sickle cell disease?
What causes sickle cell disease?
Which children are at risk for sickle cell disease?
What are the symptoms of sickle cell disease?
How is sickle cell disease diagnosed?
What are the treatments for sickle cell disease?
What are the possible complications of sickle cell disease?
How can I help my child live with sickle cell disease?
When should I call my child's healthcare provider?

Sickle Cell Disease Treatment at Children's National Hospital
From dedicated pain clinics for older children to specialized infant sickle cell care, Children’s National delivers care and support to provide a sense of well-being and normalcy to children with sickle cell disease and their families. Discover more about the treatments we offer.

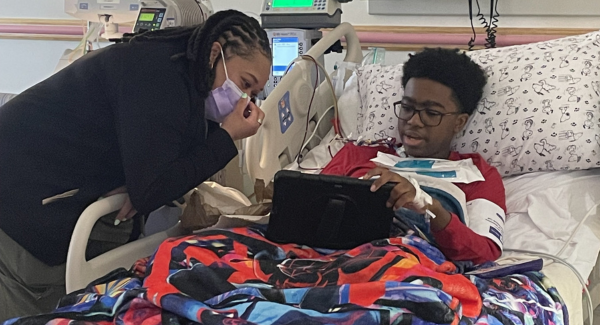
The New York Times: "First Patient Begins Newly Approved Sickle Cell Gene Therapy"
In 2024, 12 year-old Kendric received the world's first gene therapy treatment for sickle cell disease at Children's National. Approved in December 2023 by the FDA, these treatments are created by collecting and editing the patient's own blood cells and reintroducing them to the body. (The New York Times, account required)

Departments that Treat Sickle Cell Disease

Neuropsychology
Children's National Hospital has some of the world's foremost experts in care for children with complex neurodevelopmental disorders affecting the brain and central nervous system.

Help Kids and Make a Difference
Invest in future cures to help children have brighter futures.


















.jpg)
